|
Goby v2
|
|
Goby v2
|
Table of contents for modemdriver:
Return to goby-acomms: An overview of Acoustic Communications Library.
goby::acomms::ModemDriverBase defines the core functionality for an acoustic modem. It provides
To use the goby::acomms::ModemDriverBase, you need to create one of its implementations such as WHOI Micro-Modem Driver: MMDriver.
You will also need to configure the driver. At the very least this involves a serial port, baud, and modem ID (integer MAC address for the modem).
Most modems will have specific other configuration that is required. For example the WHOI Micro-Modem NVRAM is set using three character strings followed by a number. This modem-specific configuration is stored as Protobuf extensions to goby::acomms::protobuf::DriverConfig, such as micromodem::protobuf::Config. If we were using the WHOI Micro-Modem and wanted to add an NVRAM configuration value we could write
We need to connect any signals we are interested in. At a minimum this is goby::acomms::ModemDriverBase::signal_receive:
where handle_data_receive has the signature:
Next, we start up the driver with our configuration:
We need to call goby::acomms::ModemDriverBase::do_work() on some reasonable frequency (greater than 5 Hz; 10 Hz is probably good). Whenever we need to transmit something, we can either directly call goby::acomms::ModemDriverBase::handle_initiate_transmission or connect goby::acomms::MACManager to do so for us on some TDMA cycle.
The goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission message is used for all outgoing (sending) and incoming (receiving) messages. The message itself only contains the subset of modem functionality that every modem is expected to support (point-to-point transmission of datagrams).
All other functionality is provided by extensions to ModemTransmission such as those in mm_driver.proto for the WHOI Micro-Modem. These extensions provide access to additional features of the WHOI Micro-Modem (such as LBL ranging, two-way pings, and comprehensive receive statistics).
By making use of the Protobuf extensions in this way, Goby can both support unique features of a given modem while at that same time remaining general and agnostic to which modem is used when the features are shared (primarily data transfer).
All of goby-acomms is designed to be agnostic of which physical modem is used. Different modems can be supported by subclassing goby::acomms::ModemDriverBase. You should check that a driver for your modem does not yet exist before attempting to create your own.
These are the requirements of the acoustic modem:
Optionally, it can also support
The steps to writing a new driver include:
Figure out what type of configuration the modem will need. For example, the WHOI Micro-Modem is configured using string values (e.g. "SNV,1"). Extend goby::acomms::protobuf::DriverConfig to accomodate these configuration options. You will need to claim a group of extension field numbers that do not overlap with any of the drivers. The WHOI Micro-Modem driver goby::acomms::MMDriver uses extension field numbers 1000-1100 (see mm_driver.proto). You can read more about extensions in the official Google Protobuf documentation here: http://code.google.com/apis/protocolbuffers/docs/proto.html#extensions.
For example, if I was writing a new driver for the ABC Modem that needs to be configured using a few boolean flags, I might create a new message abc_driver.proto:
make a note in driver_base.proto claiming extension numbers 1201 and 1202 (and others you may expect to need in the future). Extension field numbers can go up to 536,870,911 so don't worry about running out.
Subclass goby::acomms::ModemDriverBase and overload the pure virtual methods (goby::acomms::ModemDriverBase::handle_initiate_ranging is optional). Your interface should look like this:
At startup() you get your configuration from the application (e.g. pAcommsHandler)
The full ABC Modem example driver exists in acomms/modemdriver/abc_driver.h and acomms/modemdriver/abc_driver.cpp. A simulator for the ABC Modem exists that uses TCP to mimic a very basic set of modem commands (send data and acknowledgment). To use the ABC Modem using the driver_simple example, run this set of commands (socat is available in most package managers or at http://www.dest-unreach.org/socat/):
1. run abc_modem_simulator running on same port (as TCP server) > abc_modem_simulator 54321 2. create fake tty terminals connected to TCP as client to port 54321 > socat -d -d -v pty,raw,echo=0,link=/tmp/ttyFAKE1 TCP:localhost:54321 > socat -d -d -v pty,raw,echo=0,link=/tmp/ttyFAKE2 TCP:localhost:54321 3. start up driver_simple > driver_simple /tmp/ttyFAKE1 1 ABCDriver // wait a few seconds to avoid collisions > driver_simple /tmp/ttyFAKE2 2 ABCDriver
Notes:
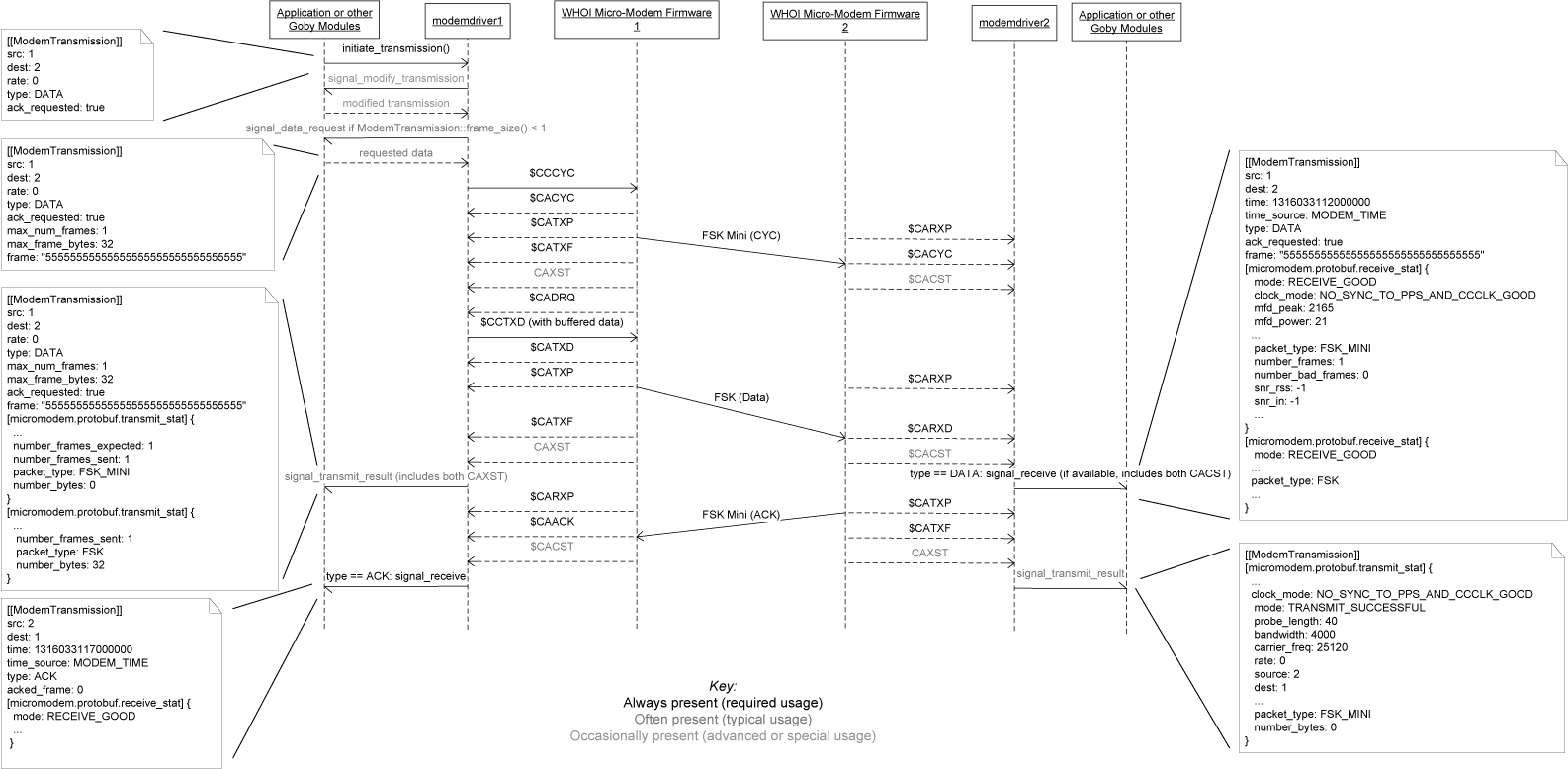
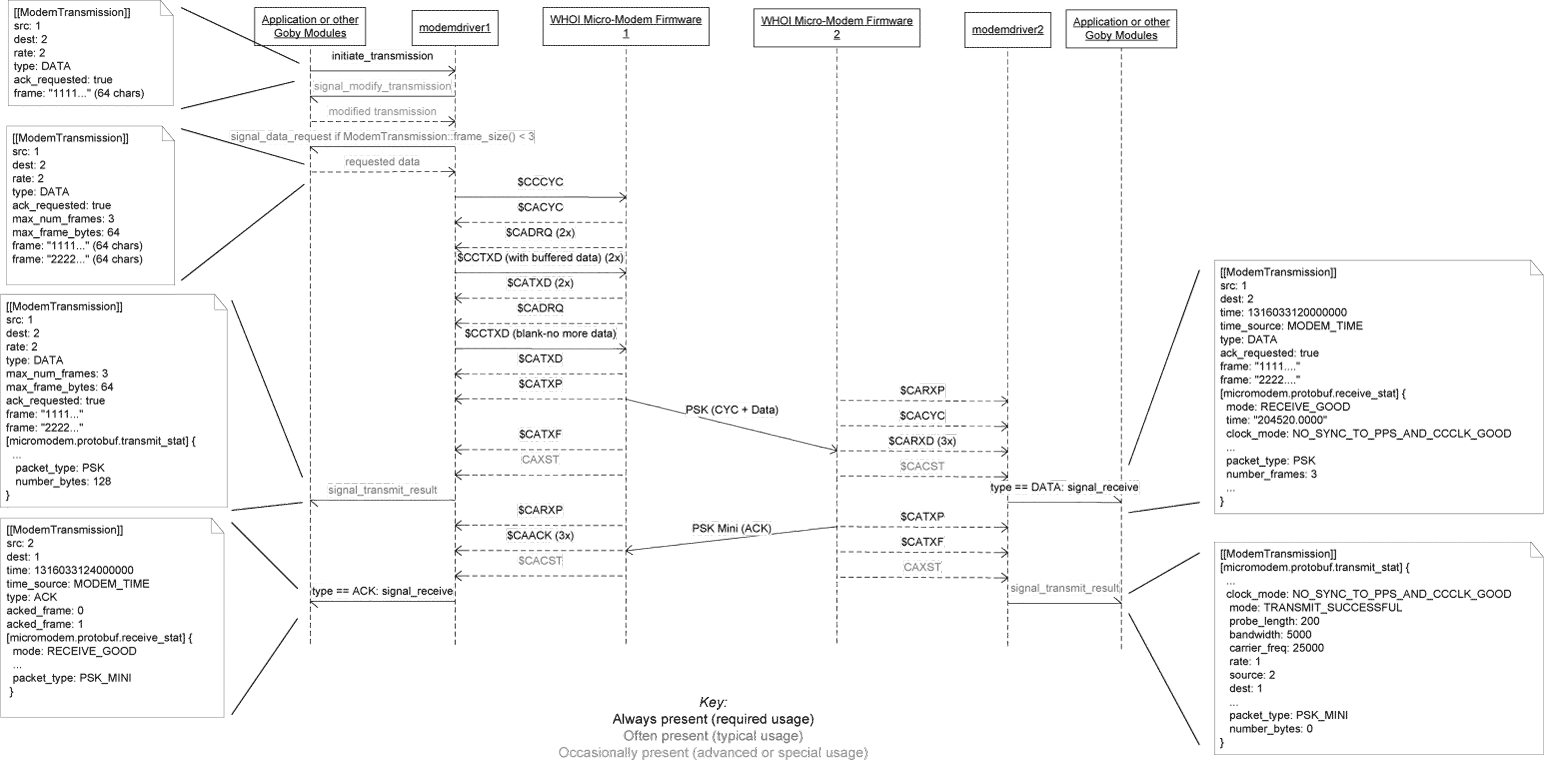
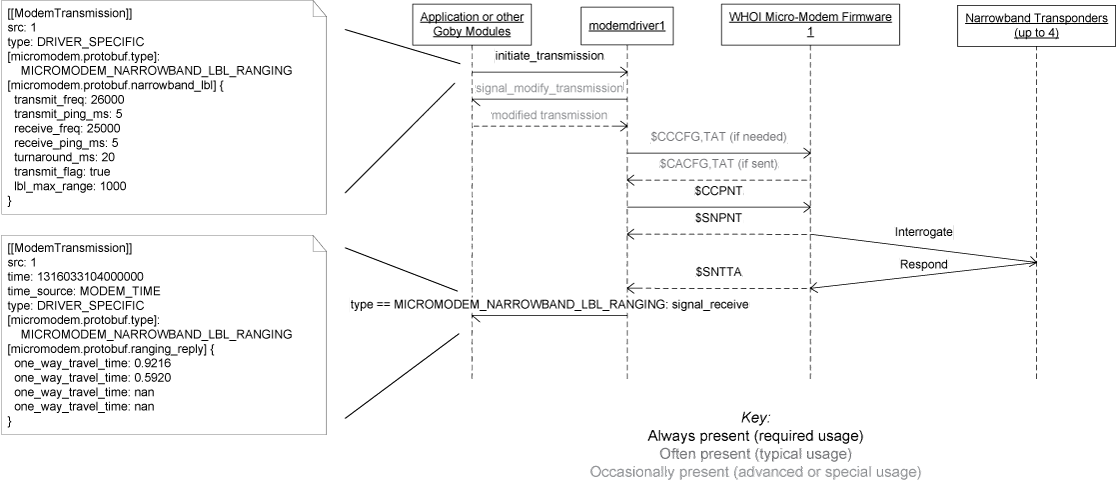
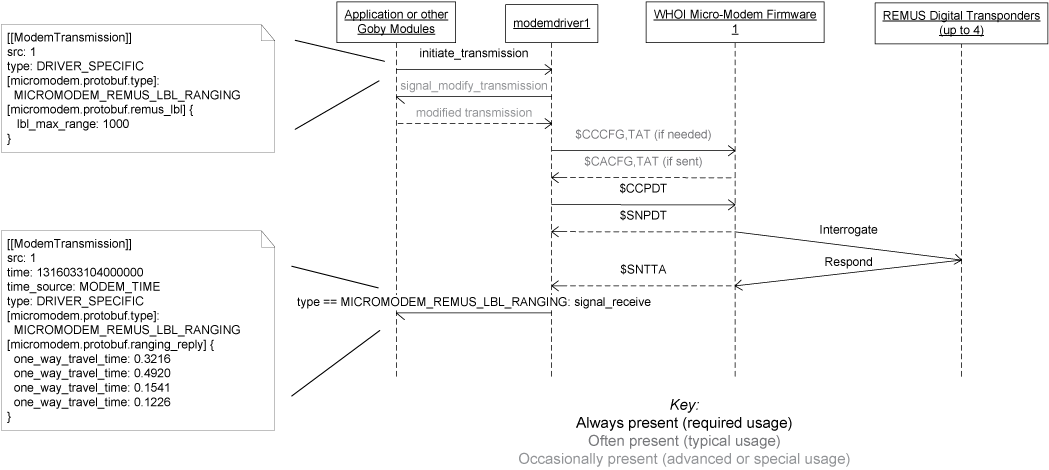
The goby::acomms::MMDriver extends the goby::acomms::ModemDriverBase for the WHOI Micro-Modem acoustic modem. It is tested to work with revision 0.94.0.00 of the Micro-Modem 1 and revision 2.0.16421 of the Micro-Modem 2 firmware, but is known to work with older firmware (at least 0.92.0.85). It is likely to work properly with newer firmware, and any problems while using newer Micro-Modem firmware should be filed as a bug in Goby. The following features of the WHOI Micro-Modem are implemented, which comprise the majority of the Micro-Modem functionality:
See the UML diagrams for a graphical diagram of using Goby for each of these features.
Mapping between modem_message.proto and mm_driver.proto messages and NMEA fields (see http://acomms.whoi.edu/documents/uModem%20Software%20Interface%20Guide.pdf for NMEA fields of the WHOI Micro-Modem):
Modem to Control Computer ($CA / $SN):
| NMEA talker | Mapping |
| $CACYC | If we did not send $CCCYC, buffer data for $CADRQ by augmenting the provided ModemTransmission and calling signal_data_request: goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.time() = goby::common::goby_time<uint64>() goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() = ADR1 goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() = ADR2 goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.rate() = Packet Type goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.max_frame_bytes() = 32 for Packet Type == 0, 64 for Packet Type == 2, 256 for Packet Type == 3 or 5 goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.max_num_frames() = 1 for Packet Type == 0, 3 for Packet Type == 2, 2 for Packet Type == 3 or 8 for Packet Type == 5 |
| $CARXD | only for the first $CARXD for a given packet (should match with the rest though): goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.time() = goby::common::goby_time<uint64>() goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.type() = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission::DATA goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() = SRC goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() = DEST goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.ack_requested() = ACK for each $CARXD: goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.frame(F#-1) = goby::util::hex_decode(HH...HH) |
| $CAMSG | Used only to detect BAD_CRC frames ($CAMSG,BAD_CRC...). (in extension micromodem::protobuf::frame_with_bad_crc) micromodem::protobuf::frame_with_bad_crc(n) = Frame with BAD CRC (assumed next frame after last good frame). n is an integer 0,1,2,... indicating the nth reported BAD_CRC frame for this packet. (not the frame number) |
| $CAACK | goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.time() = goby::common::goby_time<uint64>() goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() = SRC goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() = DEST (first CAACK for a given packet) goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.acked_frame(0) = Frame#-1 (Goby starts counting at frame 0, WHOI starts with frame 1) (second CAACK for a given packet) goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.acked_frame(1) = Frame#-1 (third CAACK for a given packet) goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.acked_frame(2) = Frame#-1 ... |
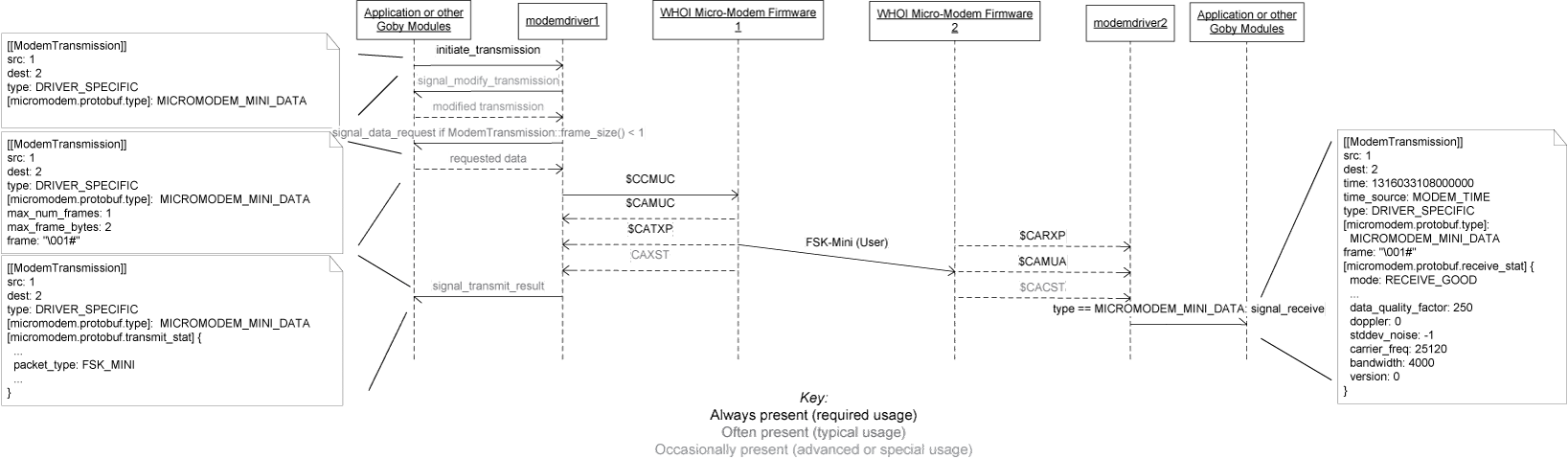
| $CAMUA | goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.type() = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission::DRIVER_SPECIFIC extension micromodem::protobuf::type = micromodem::protobuf::MICROMODEM_MINI_DATA goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.time() = goby::common::goby_time<uint64>() goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() = SRC goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() = DEST goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.frame(0) = goby::util::hex_decode(HHHH) |
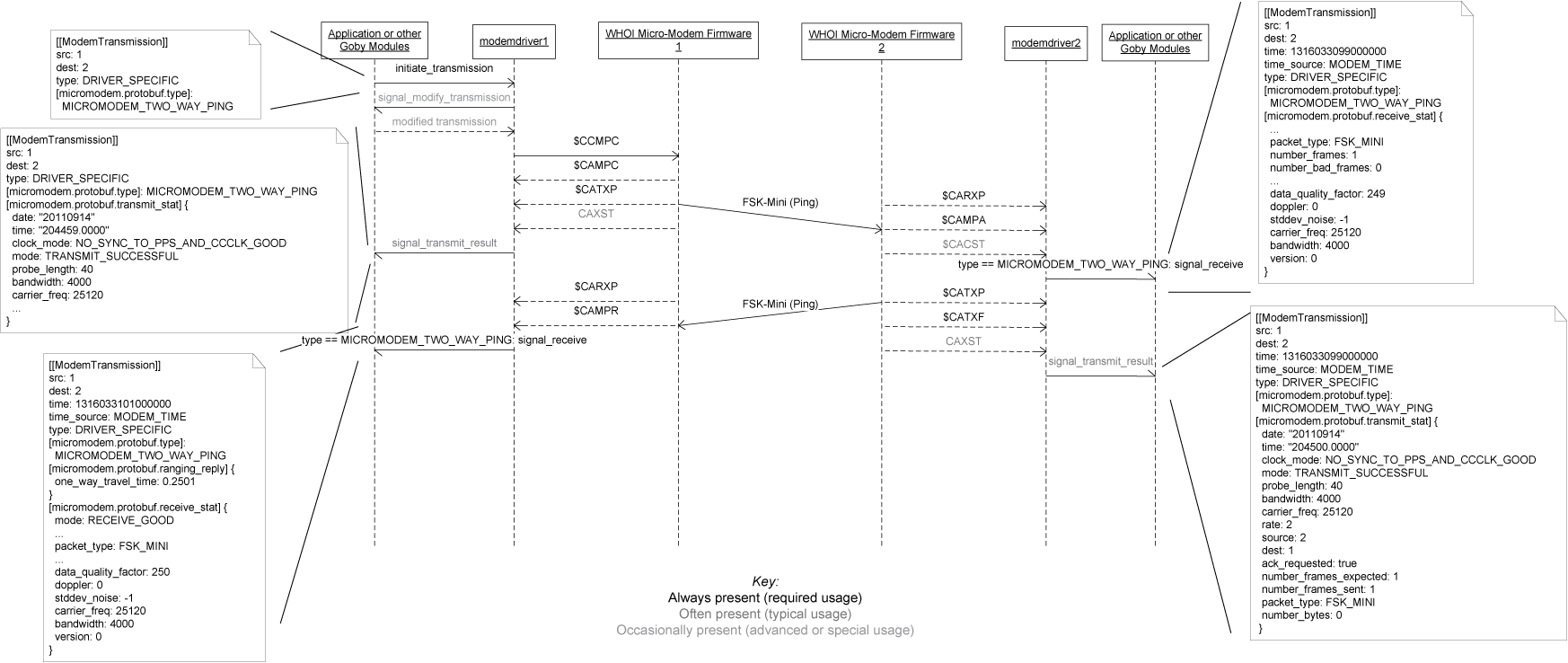
| $CAMPR | goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.time() = goby::common::goby_time<uint64>() goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() = SRC (SRC and DEST flipped to be SRC and DEST of $CCMPC) goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() = DEST goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.type() = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission::DRIVER_SPECIFIC extension micromodem::protobuf::type = micromodem::protobuf::MICROMODEM_TWO_WAY_PING (in extension micromodem::protobuf::ranging_reply) micromodem::protobuf::RangingReply.one_way_travel_time(0) = Travel Time |
| $CAMPA | goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.time() = goby::common::goby_time<uint64>() goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() = SRC goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() = DEST goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.type() = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission::DRIVER_SPECIFIC extension micromodem::protobuf::type = micromodem::protobuf::MICROMODEM_TWO_WAY_PING |
| $SNTTA | goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.time() = hhmmsss.ss (converted to microseconds since 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC) goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.time_source() = goby::acomms::protobuf::MODEM_TIME goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.type() = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission::DRIVER_SPECIFIC extension micromodem::protobuf::type = micromodem::protobuf::MICROMODEM_REMUS_LBL_RANGING or micromodem::protobuf::MICROMODEM_NARROWBAND_LBL_RANGING (depending on which LBL type was last initiated) goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() = modem ID (in extension micromodem::protobuf::ranging_reply) micromodem::protobuf::RangingReply.one_way_travel_time(0) = TA micromodem::protobuf::RangingReply.one_way_travel_time(1) = TB micromodem::protobuf::RangingReply.one_way_travel_time(2) = TC micromodem::protobuf::RangingReply.one_way_travel_time(3) = TD |
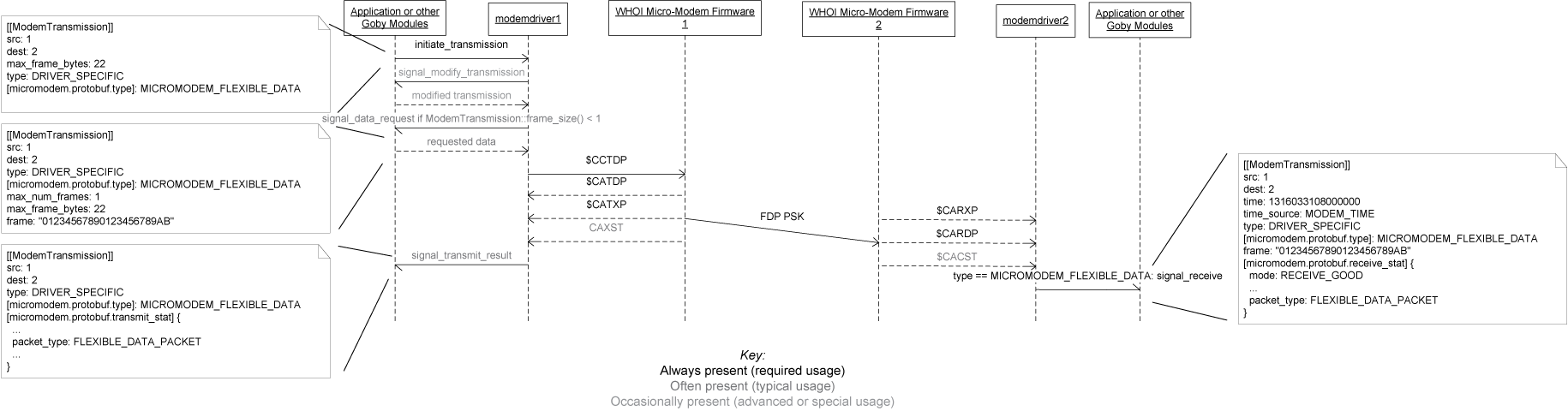
| $CAXST | maps onto extension micromodem::protobuf::transmit_stat of type micromodem::protobuf::TransmitStatistics. The two $CAXST messages (CYC and data) for a rate 0 FH-FSK transmission are grouped and reported at once. |
| $CACST | maps onto extension micromodem::protobuf::receive_stat of type micromodem::protobuf::ReceiveStatistics. The two $CACST messages for a rate 0 FH-FSK transmission are grouped and reported at once. Note that this message contains the one way time of flight for synchronous ranging (used instead of $CATOA). Also sets (which will overwrite goby_time() set previously): goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.time() = TOA time (converted to microseconds since 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC) goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.time_source() = goby::acomms::protobuf::MODEM_TIME |
| $CAREV | Not translated into any of the modem_message.proto messages. Monitored to detect excessive clock skew (between Micro-Modem clock and system clock) or reboot (INIT) |
| $CAERR | Not translated into any of the modem_message.proto messages. Reported to goby::glog. |
| $CACFG | NVRAM setting stored internally. |
| $CACLK | Checked against system clock and if skew is unacceptable another $CCCLK will be sent. |
| $CADRQ | Data request is anticipated from the $CCCYC or $CACYC and buffered. Thus it is not translated into any of the Protobuf messages. |
| $CARDP | goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.type() = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission::DRIVER_SPECIFIC extension micromodem::protobuf::type = micromodem::protobuf::MICROMODEM_FLEXIBLE_DATA goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() = src goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() = dest goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.rate() = rate goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.frame(0) = goby::util::hex_decode(df1+df2+df3...dfN) where "+" means concatenate, unless any frame fails the CRC check, in which case this field is set to the empty string. micromodem::protobuf::frame_with_bad_crc(0) = 0 indicated that Goby frame 0 is bad, if any sub-frame in the FDP has a bad CRC |
Control Computer to Modem ($CC):
| $CCTXD | SRC = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() DEST = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() A = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.ack_requested() HH...HH = goby::acomms::hex_encode(goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.frame(n)), which n is an integer 0,1,2,... corresponding to the Goby frame that this $CCTXD belongs to. |
| $CCCYC | Augment the ModemTransmission: goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.max_frame_bytes() = 32 for Packet Type == 0, 64 for Packet Type == 2, 256 for Packet Type == 3 or 5 goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.max_num_frames() = 1 for Packet Type == 0, 3 for Packet Type == 2, 2 for Packet Type == 3 or 8 for Packet Type == 5 If ADR1 == modem ID and frame_size() < max_frame_size(), buffer data for later $CADRQ by passing the ModemTransmission to signal_data_request CMD = 0 (deprecated field) ADR1 = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() ADR2 = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() Packet Type = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.rate() ACK = if ADR1 == modem ID then goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.ack_requested() else 1 Nframes = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.max_num_frames() |
| $CCCLK | Not translated from any of the modem_message.proto messages. (taken from the system time using the boost::date_time library) |
| $CCCFG | Not translated from any of the modem_message.proto messages. (taken from values passed to the extension micromodem::protobuf::Config::nvram_cfg of goby::acomms::protobuf::DriverConfig). If the extension micromodem::protobuf::Config::reset_nvram is set to true, $CCCFG,ALL,0 will be sent before any other $CCCFG values.) |
| $CCCFQ | Not translated from any of the modem_message.proto messages. $CCCFQ,ALL sent at startup. |
| $CCMPC | micromodem::protobuf::MICROMODEM_TWO_WAY_PING == extension micromodem::protobuf::type SRC = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() DEST = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() |
| $CCPDT | micromodem::protobuf::protobuf::MICROMODEM_REMUS_LBL_RANGING == extension micromodem::protobuf::type micromodem::protobuf::REMUSLBLParams type used to determine the parameters of the LBL ping. The object provided with configuration (micromodem::protobuf::Config::remus_lbl) is merged with the object provided with the ModemTransmission (micromodem::protobuf::remus_lbl) with the latter taking priority on fields that a set in both objects: GRP = 1 CHANNEL = modem ID % 4 + 1 (use four consecutive modem IDs if you need multiple vehicles pinging) SF = 0 STO = 0 Timeout = micromodem::protobuf::REMUSLBLParams::lbl_max_range() m *2/ 1500 m/s * 1000 ms/s + micromodem::protobuf::REMUSLBLParams::turnaround_ms() goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemRangingRequest.enable_beacons() is a set of four bit flags where the least significant bit is AF enable, most significant bit is DF enable. Thus b1111 == 0x0F enables all beacons AF = micromodem::protobuf::REMUSLBLParams::enable_beacons() >> 0 & 1 BF = micromodem::protobuf::REMUSLBLParams::enable_beacons() >> 1 & 1 CF = micromodem::protobuf::REMUSLBLParams::enable_beacons() >> 2 & 1 DF = micromodem::protobuf::REMUSLBLParams::enable_beacons() >> 3 & 1 |
| $CCPNT | micromodem::protobuf::protobuf::MICROMODEM_NARROWBAND_LBL_RANGING == extension micromodem::protobuf::type Ftx = micromodem::protobuf::NarrowBandLBLParams::transmit_freq() |
| $CCMUC | SRC = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.src() DEST = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() HHHH = goby::acomms::hex_encode(goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.frame(0)) & 0x1F |
| $CCTDP | dest = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.dest() rate = goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.rate() ack = 0 (not yet supported by the Micro-Modem 2) reserved = 0 hexdata = goby::acomms::hex_encode(goby::acomms::protobuf::ModemTransmission.frame(0)) |
FSK (rate 0) data transmission
 1.8.11
1.8.11